Technology is rapidly reshaping healthcare, and robotics stands out as one of the most transformative innovations. From assisting in complex surgeries to supporting patient care and rehabilitation, robotics is revolutionizing how medical services are delivered. With advances in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and sensor technology, robots are no longer confined to laboratories or factories—they are actively improving patient outcomes, reducing healthcare costs, and helping doctors perform their jobs with greater precision.
Surgical Robotics: Precision and Minimally Invasive Care
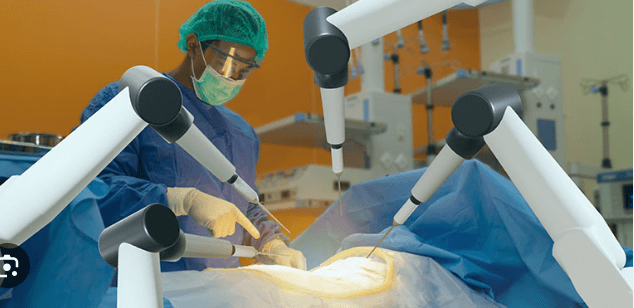
One of the most significant applications of robotics in healthcare is in surgery. Robotic surgical systems, such as the da Vinci Surgical System, allow surgeons to perform minimally invasive procedures with enhanced precision. Using robotic arms controlled by surgeons, these systems translate hand movements into smaller, more precise actions.
Benefits include:
- Smaller incisions and reduced scarring
- Shorter recovery times
- Lower risk of infection
- Enhanced visualization during surgery
Robotic-assisted surgery is now common in procedures such as cardiac surgery, prostate surgery, gynecology, and orthopedics.
Rehabilitation and Assistive Robots
Rehabilitation robots are designed to help patients regain mobility and strength after injuries, strokes, or surgeries. Robotic exoskeletons and therapy devices provide physical support, guiding patients through controlled movements to rebuild motor skills.
For example, wearable robotic exoskeletons assist paralyzed patients in walking, improving physical health and boosting confidence. Similarly, robotic arms and devices aid individuals with limited mobility in performing everyday tasks, enhancing independence and quality of life.
Patient Care and Support Robots
Hospitals and healthcare facilities are increasingly using robots for patient care and support. These include service robots that deliver medicines, transport equipment, or sanitize hospital spaces with UV light. Social robots equipped with AI can also interact with patients, offering companionship, answering basic questions, and monitoring vital signs.
In elderly care, robots can provide reminders for medication, detect falls, and offer emotional support—helping reduce the burden on caregivers and improving patient well-being.
Robotics in Diagnostics
Robotic technology is also advancing medical diagnostics. Robots powered by AI can analyze scans, blood samples, and other data with exceptional accuracy. For instance, robotic microscopes can detect cancer cells, while robotic-assisted imaging devices improve accuracy in radiology.
Such tools not only speed up the diagnostic process but also minimize human error, leading to earlier detection of diseases and better treatment outcomes.
Pharmacy and Laboratory Automation
Robotics is streamlining operations in pharmacies and laboratories. Automated robots can sort, dispense, and package medications with high accuracy, reducing the risk of errors in prescriptions. Laboratory robots, meanwhile, handle repetitive tasks such as analyzing samples, allowing medical professionals to focus on more complex duties.
This not only saves time but also ensures precision, especially in high-volume testing scenarios such as during pandemics.
Telepresence and Remote Care
Telepresence robots are bridging the gap between doctors and patients in remote areas. These robots, equipped with cameras, microphones, and screens, allow doctors to interact with patients virtually while still being present through robotic mobility.
Such technology is particularly beneficial in rural or underserved regions where access to healthcare professionals is limited. Telepresence robots also enable specialists to guide local medical staff during procedures without being physically present.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite the many benefits, robotics in healthcare also brings challenges:
- High costs: Robotic systems and maintenance can be expensive, limiting adoption in low-resource settings.
- Training needs: Healthcare staff must be trained to use advanced robotic systems effectively.
- Ethical concerns: Issues such as patient privacy, data security, and dependence on machines raise important ethical questions.
- Human touch: While robots can assist, they cannot fully replace the empathy and compassion provided by human caregivers.
Conclusion
The role of robotics in healthcare is revolutionary, offering new levels of precision, efficiency, and patient support. From surgical innovations to rehabilitation, diagnostics, and elder care, robotics is expanding the possibilities of modern medicine. While challenges remain, the integration of robotics with AI and other emerging technologies promises a future where healthcare becomes safer, faster, and more accessible. By balancing technological advancement with human empathy, robotics can truly transform healthcare for generations to come.